The Power of Financial Data: Learn About Financial Literacy
Companies, businesses, and individuals often have to make decisions that could affect overall performance and productivity. Data constantly informs these decisions, making data collection, organization, and interpretation critical.
Financial data helps businesses identify trends, analyze patterns, and provide insights that allow them to make informed decisions. Lack of financial data could lead to missed opportunities, which could negatively affect a business.
At this point, you are probably wondering, “What is the challenge?”. This invaluable financial data is available in unstructured form across the web.
But what if there is a way to transform any website into structured data? As a result, you can access a vast amount of financial data on the web. This is where residential proxies become critical. Some of its benefits include seamless data extraction, which allows you to access geo-restricted content.
This article will explore financial data, its significance to your business, challenges to obtaining data, and solutions that work just for you!
Let us dive in!
What is Financial Data?
Financial data can serve as decisive information in the modern business world. Therefore, financial reports or analysis takes place regularly. It allows businesses to organize reports to project future profits and industry growth.
Financial data is significant because it provides useful insights into a company’s financial performance. In addition, it plays a crucial role in identifying trends and possible risks associated with a decision. This data can be used to assess the performance of an organization against those of competitors. Third parties like ghost investors, creditors, and regulators may review an organization’s financial data to make an informed decision.
Types of Financial Data

Traditional data
Traditional data, as the name suggests, are the traditional sources of financial data. They include financial reports, SEC filings, and press releases. Others include assets, cash flow, income, expenses, and liabilities.
Some may argue that traditional data is more accurate. However, it is definitely slower to update.
Alternative data
Alternative data is any data that was not obtained from traditional sources. Alternative data sources include social media, internet trends, email receipts, geolocation data, and satellite imagery. This data can be used to make investment decisions because they provide a complete financial picture.
Obtaining alternative data is faster compared to traditional data. Also, they can be prone to bias, like social media sentiment analysis. This is because the results may differ from an accurate population representation.
However, many investors are embracing alternative data because it provides a unique financial perspective. Analysis by Forrester indicates that 56% of decision-makers are looking towards alternative data sources. Another study reveals that the alternative data market is expected to grow at an annual rate of 58.5% from 2021 to 2028. Therefore, the alternative data market is gaining momentum and becoming mainstream for business decision-makers.
The major ways businesses source alternative data include third-party licensing, raw data acquisition, and web scraping.
Third-party licensed parties can provide alternative data- they generate raw data like POS transactions and credit card data from other companies. These licensed third parties then process the data and organize it in a usable form, which is then sold to investors.
On the other hand, web scraping involves using tools like residential rotating proxies to get data from the internet. Businesses can benefit from this tool for some reasons:
- You can avoid website blocks by mimicking the use of a regular user
- It can bypass GEO-restricted content
- You can access any website and access any data you require
Financial Statements
Financial statements unveil the financial performance of an organization over a period. Investors often depend on this data to determine the health of a company and the amount of capital they can invest. In addition, financial data can be based on a company’s past, present, or future performance.
Let us examine some financial statements.
Income statement
This data reveals an organization’s profit and losses over a certain period. It shows revenue, expenses, and net income. A company’s net income is the result of subtracting the expenses from the revenue. As a result, investors may consider this data to determine the financial behavior of a company before risking their capital.
The income statement is a public document that reflects a company’s inflow, outflow, loss, and profit. Primary components include:
- Operating revenue
- Net and gross revenue
- Non-operating revenue
- Primary expenses, including general and administrative costs
- Secondary expenses include capital loss and loan interest.
Balance sheet
Balance sheet data represents the equity, liabilities, and assets at a specific time. It differs from the income statement as it provides an overview of the company’s financial status at a particular time. Here are some of the items outlined in a balanced sheet:
- Liquid assets such as treasury bills, money, and short-term securities
- Current assets such as prepaid expenses, inventory
- Liabilities such as tax expenses, debts (short and long-term), payable wages, and prepayments for goods/services
- Capital gains, retained income, stocks, and receivable dividends
Cash Flow Statement
As the name suggests, this statement shows a company’s cash flow over a period. In other words, it reveals the cash trail, where money comes from, and how it is spent. Cash flow is critical for all businesses as it indicates the availability of cash to invest in the company’s growth and the ability to meet short-term payments. As a result, investors are often interested in how a company manages its finances.
The statement of cash flow often reveals:
- Operational activities like income tax, account receivable, cash receipts
- Financing activities like cash from shareholders and investors, payable dividends,
- Investment activities include payments from mergers/acquisitions and fixed asset purchases for equipment or property.
Components of Financial Data
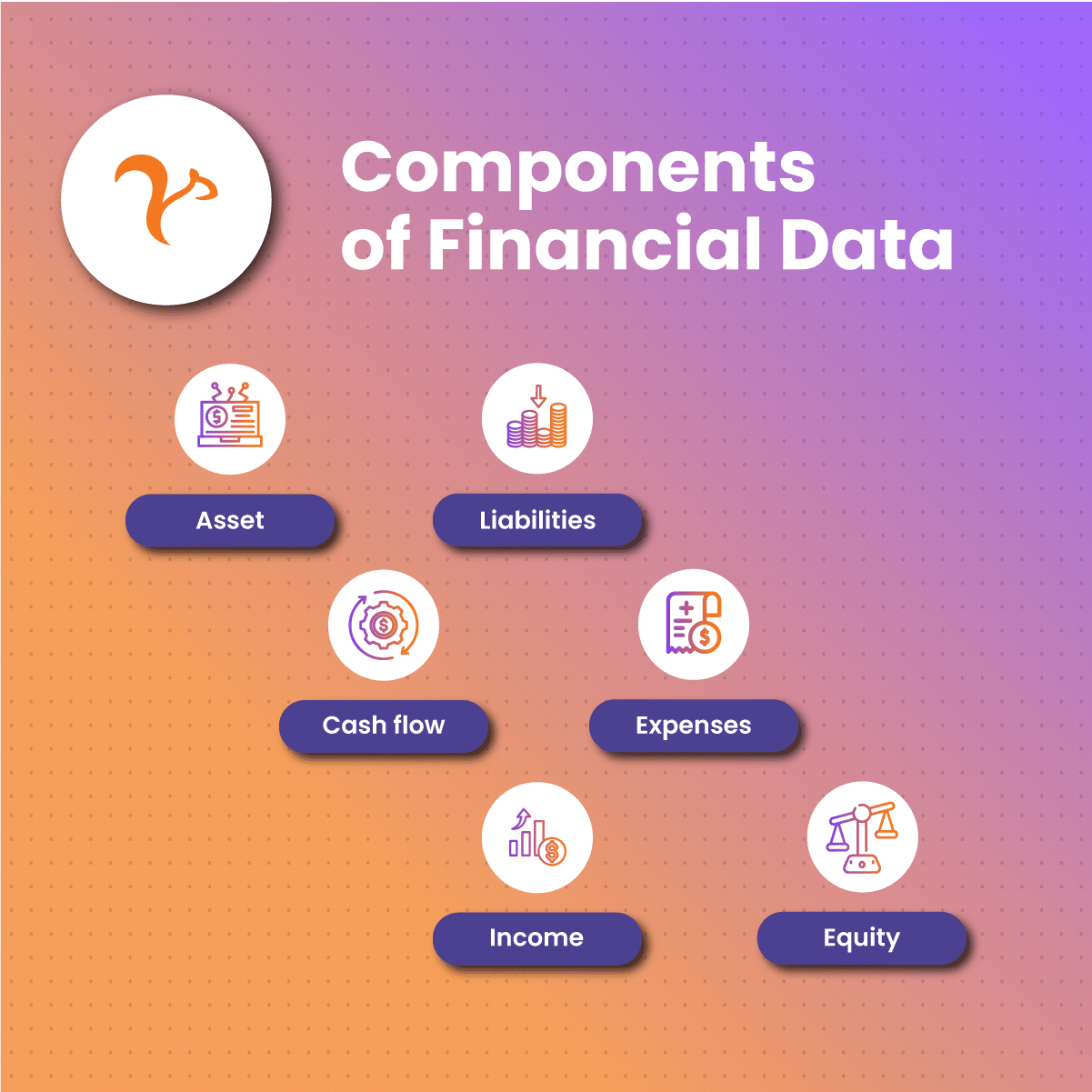
Asset
A business describes an asset as something they own and has value. In other words, an asset is something that can be exchanged for cash. Assets could be physical or intangible. Physical assets include lands, buildings, furniture, equipment, and raw materials.
On the other hand, intangible assets could include patents, copyrights, customer lists, or anything of value that does not have a physical form.
Liabilities
Liabilities are anything that demands the outflow of money. They include financial obligations such as gas for all the company’s cars. Other forms of liabilities are loans, taxes, and money received for a service/product that has not been delivered.
In other words, liabilities cause an organization to spend money without bringing in any income. A company could have short-term or long-term liabilities. The short-term liabilities can be settled within a year. On the other hand, long-term liabilities are debts that extend beyond a year.
Cash flow
Cash flow is a term that describes the movement of money in and out of a business. Financing cash flow, operating cash flow, and investing cash flow are often reported. The cash flow statement records these activities over a certain period.
Financing cash flow is money derived from business financing activities like sales of equity. On the other hand, operating cash flow is the money derived from the regular operations. Meanwhile, investment cash flow is money from return on investment.
Expenses
Businesses spend money to ensure smooth day-to-day operations of activities, and this is categorized as expenses. Other forms of expenses include interest expenses, administrative expenses, and the cost of tools and work materials.
Income
Income is the total money an organization derives from its operations. It may include sales revenue, income from rental property, and investment returns. A company is often described as profitable when its income exceeds its expenses. On the other hand, when the expenses exceed the income, the business is described as unprofitable.
Equity
The term equity refers to the percentage of a company held by shareholders. In other words, it is the residual value of its assets after clearing the liabilities. There are two types of equity-common and preferred. Common equity describes the amount held by common shareholders. On the other hand, preferred equity is held by preferred shareholders. In cases where a company’s liabilities are greater than its assets, there may be “zero equity.”
Characteristics of Financial Data
Some characteristics must be considered when organizing and making decisions based on financial data. They include:
Accuracy
Financial data must be accurate to be a useful determinant of critical decisions. Therefore, financial data must accurately represent the concept it focuses on. As a result, the data must be complete, free from error and bias. For example, data representing economic information from New York City should contain such rather than data from Ontario, Canada.
Completeness
Another critical characteristic of financial data is completeness. The data must be complete for analysts and investors to make sense of it. Incomplete data provides an incomplete picture of the financial status of a company. Therefore, it is unreliable and irrelevant.
Understandability
This characteristic defines financial data’s ability to be organized, sorted, and presented in a clear and easy-to-understand format. Therefore, the raw data should be free from difficult words and be straight to the point.
Timely
Financial data must be timely, meaning the information should be available to end users when they need it to make critical decisions. Information that comes later may not be relevant to the decision-making process.
Relevance
Financial data must be relevant, which means it should provide valuable information that allows end-users to make informed economic decisions. Data can be considered relevant if it contains information regarding past events and projects future economic trends.
Comparability
The characteristics of comparability mean that the end users of the data, such as businesses or investors, can compare the information of an entity at one time and over time.
Challenges in obtaining Alternative data
The internet is a warehouse of information, including financial data. Since the world has gone digital, businesses have websites, platforms, and apps that indirectly serve as a wealth of financial information. If this is the case, it should be easy to access this data. This is not the case because most financial data are scattered across various platforms in unstructured formats, making it difficult to extract, interpret, and use effectively.
Exploring unstructured data can be like walking in a maze without a map. Market data, economic data, and business financial statements are in various formats worldwide. Therefore, end users like investors and business managers may need help to make sense of it at a glance so that it can inform their financial decisions.
ALL HOPE IS NOT LOST!!! If you want to extract financial data, you need the help of some special tools- proxies. Here are some unique advantages of using proxies:
- ISP proxies provide lightning-fast, secure, and reliable access to data
- By-pass any CAPTCHA that may prevent data extraction.
- Automated web unlocking for efficient data extraction
- You can access websites anonymously- the website perceives your IP as a residential address, which minimizes the chances of being blocked or flagged.
- These proxies allow you to access data across various geographic locations.
Conclusion
This article has examined the significance of financial data for critical business and investment decisions. However, there are several challenges to extracting these data from their various sources.
Financial data must have specific characteristics, including timely, relevant, complete, comparable, and accurate. Therefore, businesses and individuals who understand the game of financial data need proxies to optimize data extraction. Netnut is a game-changing solution that is tailored to your specific needs. Visit us today to get started!
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers
Q1: What are the pros and cons of using a Proxy IP to extract data?
One of the primary benefits of Proxy IP is that it grants users access to specific restricted online sites and content. Some websites have anti-proxy detectors that may flag your IP address. Read a recent article here for more information.
Q2: What is data scraping?
Data scraping is a method that allows companies to retrieve data from various sources, which can be used to optimize operations and identify trends and opportunities. You can read a recent article here to get more details.
Q3: How can I choose the best proxy network for my mobile device?
Netnut provides various options to customers, including static residential proxies, rotating residential proxies, and mobile proxies. Visit us today to enhance your mobile proxy management.





