P2P Proxy: Essential Things to Know About It
Proxy servers act as a gateway between a local device or network, such as all the computers in a company, and the internet.
When you try to visit a website, your Internet-connected device doesn’t connect directly to that site’s web server. Instead, the traffic is filtered through the proxy, which is an intermediary.
As a result, proxy servers offer enhanced privacy, protect site navigation, make it easier to access location-specific content, and more. That’s why they play a key role in cybersecurity and access monitoring.
P2P proxies are used for similar purposes but offer unique features and have many other applications.
Do you want to learn more about P2P proxies, their benefits, disadvantages, and more? Read on to discover the essential things you should know about this type of network.
What Is a P2P Proxy Server?
Essentially, a P2P proxy is a proxy network where participants, or “peers,” share their resources. They act as both clients and servers.
Unlike traditional proxy models, a P2P proxy operates based on decentralization. This type of network doesn’t route data through a central server but through multiple peer nodes.
Since the network load is distributed among peers, each acts as a mini-server. Furthermore, decentralization makes the advantages of P2P proxies even more impressive.
Here’s an example:
- If a traditional proxy is used, the destination server will receive a request when a client visits a website or downloads a file. However, with a P2P proxy, the request is sent to a participant within the P2P proxy network.
The peer node that receives the request can process it in two ways:
- If it has accessed the requested data before, the peer node retrieves that information from the local cache.
- When the data isn’t in the cache, the peer node can forward the request to another peer node within the same proxy network.
In this case, the original request becomes anonymous because it goes through multiple peer nodes.
After retrieving the requested information, the response data is sent back to the client. However, the path to send the data back to the user doesn’t have to be the same as the one used to make the request.
The P2P network analyzes different factors, such as network congestion or peer nodes’ proximity and current load, to choose the best path for the response data.
How Can You Use a P2P Proxy?
A person who wants to use a P2P proxy should participate in a network that relies on the peer-to-peer model.
When using a P2P proxy, the setup process may vary depending on the network and software you choose, but these are the common steps:
- Choose a P2P network, such as a file-sharing or a blockchain network
- Download and install the right software according to the network you chose
- Set up your network connection
- Pick the files you want shared if you choose a file-sharing network or set up your wallet if you choose a blockchain network
- Connect to the network by pressing the “connect” button or just opening the software
- Start using the P2P proxy by sending or receiving transactions, searching for files to download, or uploading yours
Common Uses of a P2P Proxy
P2P proxies are used for many digital services, especially those that require higher resilience and efficiency.
Here are some examples:
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
P2P proxies’ role in content delivery networks (CDNs) has become crucial. CDNs deliver web content, including images, web pages, and videos.
When using a P2P proxy, CDNs distribute that content over a network with many worldwide servers. If there’s a request, the CDN routes the data to the server that is geographically closer to the user.
That’s possible through a P2P proxy. As a result, the distance the data travels is shorter, reducing latency for a better user experience.
P2P File-Sharing Networks
Many use P2P proxies in file-sharing networks where files come from a central server. Instead of storing files, these networks split them into pieces before distributing them across multiple peer nodes.
If someone wants to download a file, the P2P proxy allows the user to download different pieces of that file from multiple peers. This ensures the data will be available even if not all peers are. Additionally, this process increases speed and efficiency.
Blockchain Network
P2P proxies also play a key role in blockchain networks’ operation. This includes the popular Bitcoin and Ethereum infrastructures.
There’s no central server because blockchain networks are decentralized. The data storage and all transactions occur across multiple peers.
A P2P proxy routes transactions and data between peers to boost the network’s decentralization, improve efficiency, increase resilience, and enhance security.
Pros of a P2P Proxy
A P2P proxy offers multiple advantages, including the following:
- Resilience: P2P networks can handle failures even if a peer node goes down. If this happens, other peers can take over their role.
- Scalability: Each peer provides storage, bandwidth, and other resources. The more peers join the network, the higher the capacity. That’s why P2P networks are highly scalable.
- Anonymity: A P2P proxy spreads data across multiple peers, making it difficult to trace the activity back to the user who made the request.
- Efficiency: With a P2P proxy, there’s less latency because data is distributed between peers through the shortest path, which is more efficient. Additionally, these networks serve cached copies from several peer nodes, so they can handle higher demand.
Cons of a P2P Proxy
Although a P2P proxy offers many advantages, there are also several drawbacks. These are:
- The P2P proxy setup process can be complex and time-consuming. It requires a deep understanding of specific protocols and underlying technology.
- While this technology isn’t illegal, P2P networks can be used for unlawful activities, such as sharing copyrighted content.
- A P2P proxy enhances anonymity and security, but that doesn’t mean there are no risks. A malicious peer can alter data when routed through the network if it manages to join it.
- Although the performance of a P2P proxy is often optimal, it depends on the number of available peers and other factors. Performance may be affected if there aren’t enough peers or the existing ones have slow connections.
Are P2P Proxies Better than Other Types of Proxies?
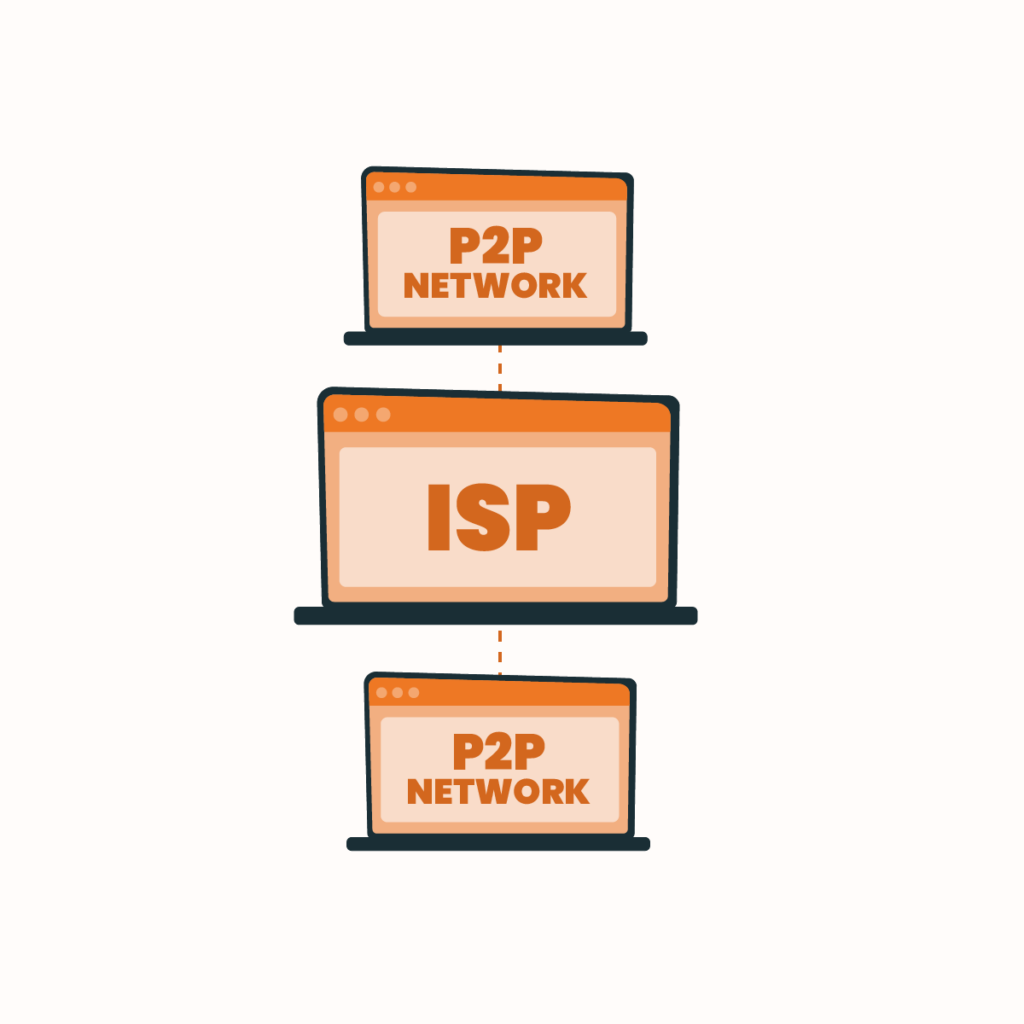
As mentioned, P2P proxy servers distribute data across multiple participants, known as “peer nodes.” However, many other types of proxies have different uses and purposes.
The forward proxy, for example, acts as a middleman between the client and the internet, just like the P2P proxy. It doesn’t validate the request and sends it directly to a web server but evaluates it and takes the necessary actions before routing this data to the chosen destination on behalf of the user.
There are also unblockable mobile proxies. They use several IP addresses associated with specific mobile devices to enable connections from different locations, facilitating access to geo-restricted content.
Unlike these types, P2P proxies don’t have just one server handling all requests and responses. Because of this decentralization, they’re more efficient, resilient, and scalable.
However, other proxies could offer even more benefits, such as residential proxies with ISP connectivity.
ISP Residential Proxies
An ISP proxy doesn’t connect to an end-user device but provides the IP address of an Internet Service Provider (ISP), allowing users to select a specific location. In other words, you can use a US proxy and surf the web as if you were in this area.
ISP proxies guarantee that users receive their IP address from a trusted residential device.
There are two types:
- Static: With static ISP residential proxies, users can access a site from a unique static IP address. They’re less customizable, and there’s no rotation.
- Rotating: High-speed rotation residential proxies exchange IP addresses from a pool with multiple options when a new request is made. As a result, the target website receives data from a proxy, getting a log from different geolocations.
Proxies with ISP connectivity could be a better option than P2P proxy servers, especially when it comes to web scraping, market research, data gathering, ad verification, and brand protection.
This proxy offers anonymity, privacy, and better security since it ensures that no device is used and traffic isn’t distributed on such devices.
Conclusion
There are many types of proxies, including those based on the peer-to-peer model. A P2P proxy offers several advantages, such as enhanced privacy, security, resilience, and scalability.
However, its performance isn’t always consistent, and it can pose several security risks. Therefore, you should consider the pros and cons of each type of proxy and evaluate other options to choose the best one based on your needs and preferences.
FAQs
What Is the Difference Between a P2P Proxy and a Proxy With ISP Connectivity
The main difference lies in how the data is routed from the user to the target website or network. A P2P proxy distributes data across multiple peers. Therefore, ISP proxies often offer fewer server locations.
However, a direct ISP connection doesn’t connect to the end user’s device but sources an IP address from a trusted residential device.
How Can a P2P Proxy Improve Security?
Since a P2P proxy distributes the data across several peer nodes, it’s difficult for attackers to take advantage of a single point of failure.
However, P2P networks are decentralized, so they face data use and integrity issues.
How Can I Set Up a P2P Proxy?
To set up a P2P proxy, you may need to install specific software and choose and configure your network connection. However, the steps may vary depending on the service you are using. If you need more information about this, don’t hesitate to ask your provider.