HTTP Vs. HTTPS and SSL Vs. TLS: Know the Difference
Whether you’re reading an article or checking out the URL link in the address bar, you may have come across HTTP and HTTPS. This may have raised some questions. Why is there a security warning when you visit an HTTP website? Why do developers insist on having HTTPS instead of HTTP?
In this article on HTTP vs. HTTPS, we will go over these two standard protocols and how they’re different from one another. Keep reading until the end, as we will also explore SSL and TLS certificates, the importance of authentication of a website’s server, and how Netnut can help businesses.
Let’s get started!
What Is HTTP?
Hypertext Transfer Protocol or HTTP is a basic protocol and syntax for presenting information that is transmitted over the Internet. It is a standard that defines the format of the communication between a web client and a web server.
There are two main types of HTTP messages, and these include the following:
- Requests: Whenever you visit a website, your computer sends information over to the website’s server. HTTP requests refer to the interaction generated by the user’s browser. If you click on a webpage after a quick Google search, for example, the browser will generate an HTTP request to get the information that is necessary for rendering the webpage.
- Response: When a website’s server receives an HTTP request, it will generate an HTTP response. The main purpose of the response is to provide the client with the resource they are requesting.
What Is HTTPS?
When you read the title of the article” HTTP vs. HTTPS,” you might be wondering why we’re making the comparison when the two sound similar.
Although the two might look and sound similar, they’re much different than you think. HTTPS is an extension of HTTP, and the additional “S” stands for “secure.” When the website uses TLS or SSL certification, it uses HTTPS instead of HTTP.
HTTPS is widely used on the Internet due to the secure communication it provides. The protocol encrypts the data exchanged between the client and the server, protecting against man-in-the-middle attacks.
If you want to read more on HTTPS, don’t forget to check out our blog on the five reasons to choose HTTPS proxies over SOCKS5.
HTTP vs. HTTPS: What’s the Difference?
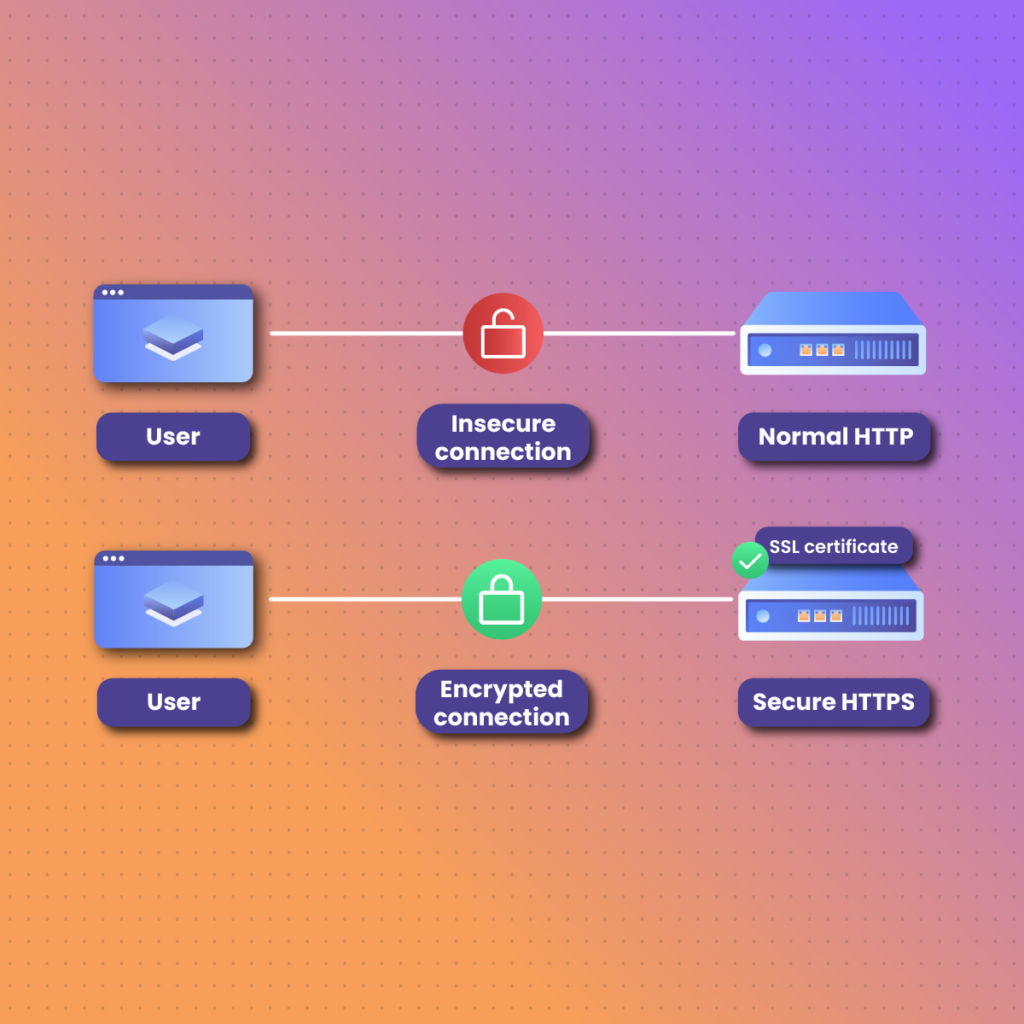
There are many differences between the HTTP and HTTPS protocols. If you visit a website, the requests and responses between the client and server on an HTTP protocol are not secure. Anyone monitoring the session can easily read the formatted information, which can put the user at risk.
A cybercriminal or threat actor who gains access to such information on an HTTP protocol can identify what the communication is about and use it for their benefit.
An HTTPS protocol is much more secure, as it encrypts and decrypts data exchange between clients and servers. If a cybercriminal is monitoring an Internet session, they’ll see a sequence of numbers and letters instead of the formatted information being exchanged.
Another major difference between the two protocols is that HTTPS uses port 443. On the other hand, HTTP uses port 80, which is a default port for unsecured protocol.
It is essential to use a secured connection or an HTTPS protocol when sending sensitive information; otherwise, the man-in-the-middle could gain access to the data.
HTTP vs. HTTPS: SSL and TLS Certificate
Web owners must enable SSL and TLS certificates if they wish to ensure security across the communication made between the client and the server.
These two types of certificates play a significant role in helping users identify whether they’re on a secure webpage. Let’s go over the differences between the two.
HTTP vs. HTTPS: What Is an SSL Certificate?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer, which is a digital certificate that enables an encrypted connection. It also authenticates the website’s identity. An SSL certificate creates an encrypted link between the website’s server and the client.
To secure online transactions and protect the user’s personal or financial information, companies and businesses must add SSL certificates to their websites. It contains a public key that encrypts the information and a private key that decrypts the data being exchanged.
Simply put, an SSL certificate prevents a threat actor from reading the information exchanged between the two systems and modifying it. The best way to identify whether the website you’re on is using an SSL certificate is by looking for a padlock next to the URL in the address bar.
If there is no padlock icon next to the URL, the browser will warn the user of an unsecured connection, prompting them to either close the website or proceed forward despite the risks.
HTTP vs. HTTPS: What Is a TLS Certificate?
Over the years, there have been many different versions of the SSL certificate. However, most of them faced security troubles until the launch of TLS.
TLS (transport layer security) is a digital certificate that is an improved version of the SSL certificate. By using a more robust security mechanism, a TLS certificate encrypts data exchanges much better than the outdated SSL.
It’s important to note that since TLS is an improved version of the SSL, it is also referred to as SSL. Most secure websites use this digital certificate, as the original SSL certificate no longer exists.
HTTP vs. HTTPS: What Are the Different Types of SSL/TLS Certificates?
There are three main types of SSL/TLS certificates, and these are as follows:
Domain Validated (DV) Certificates
These certificates offer basic encryption and validate that the certificate applicant has control over the domain. They are the quickest to obtain and are typically used for personal websites and blogs.
Organization Validated (OV) Certificates
OV certificates provide a higher level of trust, as they require the Certificate Authority (CA) to validate the domain ownership and verify the organization’s identity.
An OV certificate is popular among businesses and organizations.
Extended Validated (EV) Certificates
EV certificates provide the highest level of trust and security. They involve a rigorous validation process that includes verifying the organization’s legal identity.
These types of security certificates are often indicated by a green address bar in web browsers, providing a visual representation of trustworthiness. They are often used by e-commerce websites and financial institutions.
HTTP vs. HTTPS: What Is the Importance of an SSL/TLS Certificate?
Not secure website example:
Secure website example
An SSL/TLS certificate is important for many reasons, some of which include the following:
It Establishes a Website’s Trustworthiness
An SSL/TLS certificate is essential for a webpage owner, as it helps establish the website’s trustworthiness.
Any website with a green padlock in the address bar is an indication that the webpage is secure for the user to visit. This can give them confidence, knowing that anyone monitoring the session cannot decrypt the data exchanged between the client and the server.
A website without an SSL or TLS certificate can be a warning sign for users. This can lead to reduced traffic, which can not only affect the business’s revenues but also generate a bad image for the brand.
It Protects the User’s Data
Websites without an SSL or TLS certificate are a sign for users to remain cautious. Individuals with malicious intent could read the information exchanged, allowing them to use the data for their own benefit.
Take financial institutions as an example. If a bank’s website does not have an SSL or TLS certificate, it puts the user at risk. Whenever users log into their banking accounts, they risk getting their credentials stolen by threat actors or others monitoring the Internet session.
This is why financial institutions get the highest level of security certification to ensure that their client’s data remains protected at all times.
It Helps with Search Engine Rankings
When ranking websites, search engines like Google give preference to websites that already have an SSL or TLS certificate. Adding a security certificate to your website can help improve its visibility and search engine optimization.
It May Be Required for Compliance
Some countries have data regulation requirements that require website owners to add an SSL or TLS certificate to their websites. General Data Protection Regulation in Europe, for example, requires websites to protect their visitors with SSL certificates.
It’s important to note that not all websites need SSL/TLS certificates. The regulatory bodies require websites that exchange sensitive information to have some form of security to protect their visitors.
HTTP vs. HTTPS: How Does an SSL/TLS Certificate Encrypt Responses and Requests?
In this article on “HTTP vs. HTTPS,” we’ve gone over the two standard protocols, the security certificates, and the benefits of having an SSL/TLS certificate on a website.
However, after reading through all that information, you may be wondering how an SSL or TLS certificate works in regard to the HTTP responses and requests.
A TLS certificate uses an advanced technology that is commonly referred to as “public key cryptography.” This is a security method that encrypts data using two different types of keys. Let’s go over how it works.
A website with an SSL/TLS certificate shares the public key with the client’s device. When a visitor visits a secured website, the server and the client’s device use the public and private keys to generate new session keys. This is important in encrypting the communication between the two parties.
Anyone who intercepts the communication between the two devices following the session key will see a random string of numbers and alphabets instead of readable plain text.
HTTP vs. HTTPS: Does HTTPS Help Authenticate Web Servers?
When the Internet began, the people behind HTTP had other priorities instead of security, which is why they never considered the level of trust associated with websites.
However, with the rise in cyberattacks, there was a need to establish a website’s trust, which is where HTTPS comes in.
Authentication is essential on the modern-day Internet. If you’re buying alcohol at a supermarket, for example, the vendor may ask you to show your ID card to check whether you’re of legal age. The same principle applies to the Internet. A private key confirms the identity of the server.
The authentication process (private and public keys) on a website prevents many different types of cyberattacks, including the following:
- On-path attacks
- DNS hijacking
- BGP hijacking
- Domain spoofing
Netnut Can Help Secure Your Online Business!
With the constant threat of cybercriminals on the Internet, running a business without proper online security can adversely affect its operations and the company’s customers. It is crucial for businesses to invest in advanced security solutions to prevent breaches or other types of malicious activities.
Netnut’s architecture ensures speed and stability while guaranteeing the quality of its service. It has many different products for companies, including static residential proxies, rotating residential proxies, ISP proxies, mobile proxies, and many more.
Not only does Netnut ensure seamless browsing, but it also helps companies gain valuable insights by assisting in SEO monitoring and SERPs tracking, market research, web data extraction, and social media management, among others.
Claim your seven-day free trial to see whether Netnut’s US residential proxy or any other proxy product is the right fit for your business!
Final Thoughts
We hope that this “HTTP vs. HTTPS” article can help you understand the difference between the two standard protocols. Having a secure website is not only beneficial for your business but also for your clients.
Investing in an SSL or TLS certificate can bring a certain trustworthiness to your company’s website. It can also protect your clients from cyber criminals who are looking to steal sensitive information.
Besides an SSL or TLS certificate, businesses must invest in advanced security solutions like Netnut to ward off other threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here, we’ll answer all the commonly asked questions pertaining to HTTP vs. HTTPS.
How Does HTTPS Encryption Work?
HTTPS uses an SSL/TLS encryption to scramble data. If you send your credit card details over HTTPS, for example, they become unreadable to anyone trying to intercept the data.
Can You Switch from Your Existing HTTP Website to HTTPS?
After reading our article on “HTTP vs. HTTPS,” you may be wondering whether you can transition to HTTPS.
You can migrate to HTTPS by obtaining an SSL/TLS certificate and configuring your server accordingly. There are many hosting providers that can help you with the transition.
Is Obtaining an SSL/TLS Certificate Expensive?
The price of an SSL/TLS certificate can vary depending on certain factors, including the number of domains, validation process, and warranty, among others.
On average, an SSL/TLS certificate can cost around $60 a year, but it can go all the way to $1,000 or more annually.