A Complete Guide To SSL Proxies
Amongst the numerous varieties of proxies available in the market, one variant that is worth considering is the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) proxy. Like other proxies, SSL proxies are intermediaries, offering a high level of encryption, anonymity, and awareness against possible security threats online. An SSL proxy, also known as a Secure Sockets Layer proxy, is a type of proxy server that provides an additional layer of security for internet communications by encrypting data between the client and the server.
In this article, we will dive deeply into what an SSL proxy is and how it works. Also, we will explore different types of SSL proxies, their major benefits, some practical use cases, and relevance. And lastly, we will discuss briefly possible setbacks of the SSL proxy, and compare it with VPNs.
What Is A SSL Proxy?
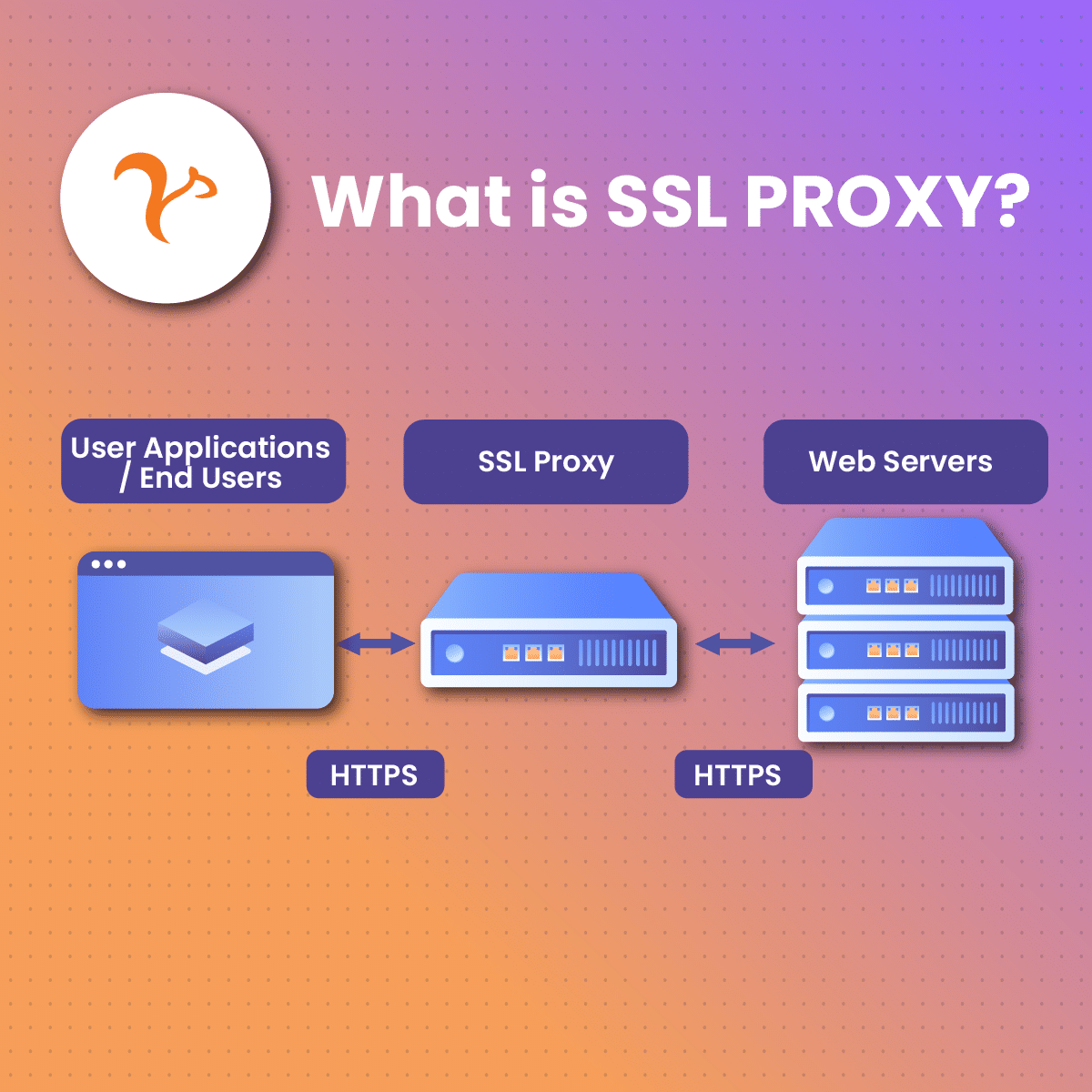
An SSL (the acronym for Secure Sockets Layer) proxy refers to a proxy server that utilizes the SSL protocol primarily for encoding (encryption) and decoding (decryption) services. SSL proxies act as intermediaries, ensuring that sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card details, and personal data, remains protected from potential eavesdroppers and cyber threats during transmission. By utilizing SSL (and its successor, TLS – Transport Layer Security), these proxies provide robust encryption, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to intercept and decipher the data being exchanged.
The primary function of an SSL proxy is to handle SSL encryption and decryption. When a client initiates a connection to a secure website, the SSL proxy intercepts the connection request. It then establishes a secure connection with the client, decrypts the data for inspection or filtering, and re-encrypts it before forwarding it to the destination server. This dual process of encryption and decryption ensures that data remains secure while allowing the proxy to perform necessary functions such as content filtering, monitoring for malicious activity, and enforcing security policies.
SSL proxies are commonly used in various scenarios to enhance security and compliance. Organizations often deploy SSL proxies to monitor and control employee internet usage, ensuring that sensitive corporate data remains protected and that employees adhere to internet usage policies. They are also used to prevent data leaks by inspecting outbound traffic for sensitive information that should not leave the corporate network. Additionally, SSL proxies are vital in environments where secure communication is paramount, such as financial institutions, healthcare organizations, and e-commerce platforms. By providing a secure layer of encryption, SSL proxies play a crucial role in maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of online communications.
SSL proxies are also known as the HTTP proxies which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocols. This is because HTTP proxy servers often utilizes the HTTP protocols over the SSL. So far, the HTTP has become the standard for many websites because of the guaranteed increase in level of privacy and security.
How Do SSL Proxies Work?
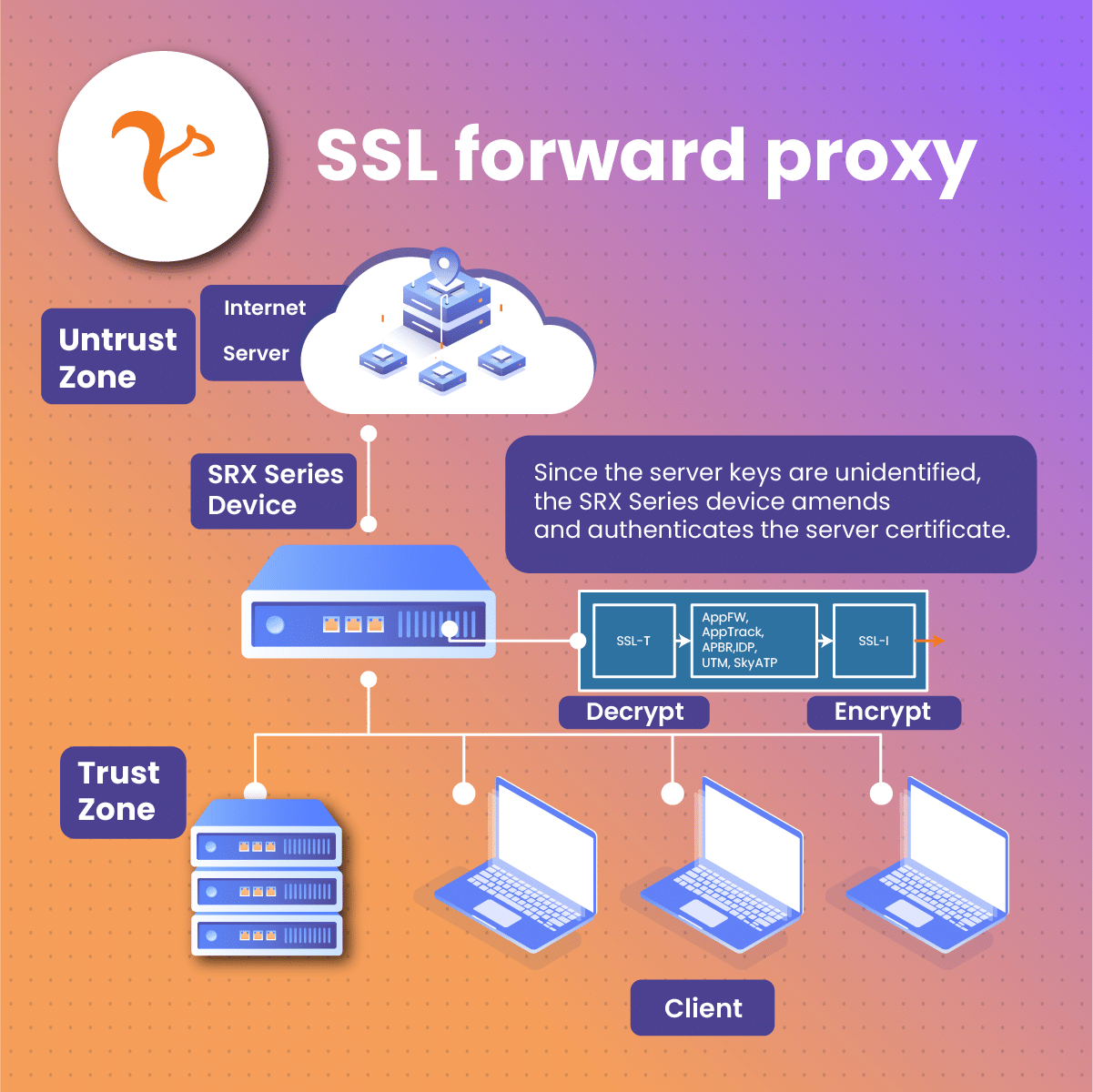
SSL proxies are positioned as an intermediary to manage the SSL traffic between the user (client) and the web (server). It helps to oversee all SSL interactions, prioritizing security between the server and the client. SSL proxy permits or obstructs connections following its filter guidelines, and in some cases, decodes incoming SSL traffic.
Let’s explore the main steps in SSL filtering:
- SSL proxy obstructs contacts from the user over Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 443.
- It does a follow-up SSL mediation with the server, representing the user.
- It inspects the certificate forwarded by the server end. In situations where the certificate is detected to breach certain expectations, entry into the server will be restricted.
- Where the certificate is detected to be compliant, the SSL proxy will review its filter guidelines such as:
- Restricting contacts without decoding
- Permitting contact without any form of decoding.
- Or simply decoding traffic which will later be assessed by the next set of filter guidelines.
- If the decode action is taken, the SSL proxy advances to develop a certificate imitation which is then forwarded to the user that will validate it. If the forwarded certificate from the mediator is yet to be installed in the receiving system, and tagged as authorized, an error response will surface.
- If the certificate has been installed and tagged as authorized, the connection will be secure. Other protection software, such as the antivirus and antispam, will be adopted
The last two steps are only applicable in cases where filtering with SSL traffic decoding is adopted.
Different Types of SSL Proxy
There are two main variants or types of SSL proxy, each of which is dedicated to act as a shield to each connection end. There are a few different types of SSL Proxies such as:
The First Variant of SSL Proxies
This variant of SSL proxy is also referred to as the “Forward SSL Proxy.” Its major function is to safeguard the user’s side. Similarly to what we initially explored, the forward SSL proxy stands as a link between the outer server and the inner user. It focuses on converting coded inputs into comprehensible languages and examines traffic going into the web space. In simple terms, it ensures that every data is marked safe before it is sent out of your local system.
The Second Variant of SSL Proxies
This variant is called the incoming or reverse proxy. It is simply the opposite of the forward SSL proxy. It helps to direct incoming traffic from data being transmitted from the web to your device. Its major target is to wade off possible threats that come with the data before it’s sent to your local device.
Benefits of the SSL Proxy
The benefits of the SSL proxy in the digital space cannot be overemphasized, especially when compared with previously developed HTTP proxy. Let’s explore some of the benefits below.
- SSL Proxy is comparably safer: SSL certificates adopt an end-to-end encryption connection between the user and the server, inferring that in a situation where traffic is interrupted, there is zero digital chance for the intruder to decode the data. This simply means leaked data is as good as meaningless to the intruder as he is not equipped with the keys to decode the encrypted information. Such an approach is necessary for sensitive interactions like customers’ online banking activities.
- SSL Proxy has an Improved Anonymity Feature. The presence of the SSL proxy as an intermediary creates a gap between end users and the external server. Such a gap enclosed in coding and decoding processes gives a higher degree of anonymity. The older version of the SSL proxy (HTTPs) contained zero traffic coding. This paved the way for transmitted information to be understandable, thereby making it susceptible to interruptions by mediators during the transfer process. This common attack pattern is referred to as a Man in the Middle (MitM) exploitation. It appears to have been a major setback in the web space as IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence Statistics in 2018 reflected that over one-third of the attacks of unexpected vulnerabilities included MitM exploitation.
- SSL Proxy provides improved supervision. In contrast to many other protocols, SSL proxy offers a heightened stage of personalized security supervision. Certain security guidelines are initially identified and, thereafter, executed at the SSL proxy stage.
- SSL Proxy Offers applaudable visibility. When enclosed data traffic arrives on the server end, it is likely to comprise system attacks that can be set off. SSL proxy acts as a hub where these possible attacks can be detected and set off before they get into a sensitive space. This proxy guarantees that vulnerabilities that can pave the way for an attack are not allowed to pass through or be transmitted undetected.
Practical Use and Relevance of the SSL Proxy
The internet has been more than generously dominated as the current generation has adjusted their everyday day life to include it. In that light, it has become crucial that it fits in as a safe space for all.
SSL proxy is developed to offer a wide range of possibilities that push for a safer and more secure web space and this has led many individuals and companies to purchase this proxy variant. Let’s take a look at some of the relevance of SSL proxy:
- Financial information transmission. Various investment firms generate and gather distinctive information points to transform how they can leverage data. When one such investment firm partners with another firm, there may come a time when they may need to transfer data as a form of business interaction. At that time, the information to be transmitted is required to be sent without any form of interception from rival firms as it may negatively impact their leverage ability. SSL proxy end-to-end encryption feature is the answer as it can offer these firms the major value in that scenario.
- Improving access to trans-regional websites. Diverse sites on the internet tend to restrict certain content to only users in that region, therefore, blocking out users from other regions. For this reason, many individuals have opted for proxy to increase their access to global information rather than accept the limitations. For example, some people employ the SSL proxy features to get access to certain Spotify content or even YouTube content.
- Development of brand protection measures. Proxies, such as the SSL, enable you to securely escape geo-blocking setup as well as develop a safe connection to supervise your brand image in the online space. With your setup, your brand’s online presence is marked safe from the likes of copyright infringement and domain squatting.
- Overseeing online accounts. Unwanted social media information release rubs off as a severe risk, be it a firm’s information, IP logs, and so on. The safe and anonymity feature of the SSL proxy makes it a trusted option for firms to choose to effectively oversee their online presence.
- Monitoring advert validation and performance. The online space is filled with fraudsters who utilize certain techniques to falsify advert traffic. What this suggests is that a significant number of advertisements do not exactly land on real social media pages, leading to losses for online-dependent businesses. Firms have now devised the method of adopting proxies to anonymously validate adverts to spot the fraudulent ones and also observe advert performance.
- Restrict pop-up adverts. It appears that almost every website contains adverts, in recent times, and that can be quite an issue to work with. The SSL private proxy can assist with such a challenge as its setup operates to help remove adverts, mostly from frequently visited sites.
- Blockchain safety support system. Blockchain technology houses diverse applications and serves as a space to facilitate the issuance of licenses for digital properties. Taking note of its underlying complicated nature, recent blockchain-dependent outlets may do better to interact with the external web through the SSL proxy. This will act as a blockchain support system to secure against certain attacks.
- You are getting access to limited items. If you are looking to bypass certain restrictions by changing your IP address, the SSL proxy will be a sure bet. Businesses often put out a limited series of their items in specific locations. Such items can only be reviewed by individuals in that location. However, being able to change your IP address will give you access to such items as well.
- Boosts the performance of online websites. People who run online sites will find the SSL proxy beneficial as it helps to boost the running of the site. How is this made possible? The proxy helps to empty SSL codes as well as develop a cache memory for content that is often accessed. This can lead to a boost in your site’s operation performance for a better experience.
SSL Proxy – Possible Setbacks
Of course, SSL proxy offers a variety of benefits and functions that significantly assist the digital space. While the proxy can be of tremendous use to an individual or firm, it is also prone to a few setbacks. Let’s take a look.
- Compatibility setback. Not all online sites are set up to accept the SSL proxy. Some local networks might not be compatible with the SSL proxy, and some sites with an overly advanced development might not conform to functioning with your SSL proxy. When faced with such setbacks, one solution could be to work on the proxy settings and reconfigure or you could simply purchase a compatible proxy.
- High cost of setup and servicing. Configuring a proxy is generally not very cheap. While big firms may not struggle to get it, we cannot say the same for smaller corporations. This is so because the proxy attracts diverse expenditures that go beyond just getting it.
- Technical nature of configuration. Proxies can be quite technical to configure, sometimes. While they have been automated to perform certain functions, improper configuration can cause a setback in it’s performance.
- Performance setback. A proxy that is not configured appropriately may begin to underperform. How does this happen? The proxy is expected to help secure all of your data from being exposed or understandable to hackers. If such a function is not efficiently carried out, then there may be a performance setback. One solution to such an issue could be to optimize your settings or opt for a better version server.
SSL Proxy Versus VPN: Are they the same?
VPNs, known as virtual private networks offer similar functions as the SSL proxy. However, both of them operate in different routes.
SSL proxy focuses on restricting and filtering web traffic and VPNs focus on encoding and channeling web traffic. SSL proxies are typically less superior in terms of security but they offer a more swift and heightened performance.
Wrap Up
Proxies, since its introduction, have focused on salvaging many online hitches and the SSL variant is no different. It is evident that the importance of choosing it can not be overstated. With the above-listed benefits and relevance, it sure is an excellent option for both individuals and public and private firms that prioritize privacy as well as security when dealing with the online space. Whether as a backup or as a main security option, SSL proxy promises safety against the many internet vulnerabilities that a lot of firms have faced in an attempt to strengthen their online presence.
Frequently Asked Questions About SSL Proxies
Can the SSL proxy become an issue?
SSL proxies are prone to a few hitches. For example, if your proxy is not set up appropriately, there might be some performance challenges like comparably slow internet load times. To solve such an issue, you may need to reconfigure some of its settings or opt for a better-performing server.
Are all websites compatible with the SSL proxy?
Not all internet sites are designed to be SSL proxy compatible. Sites with less advanced security setups are more likely to function well with this proxy variant compared to those with high-security setups. It is recommended that you reconfigure your proxy settings if you need it to be compatible or you could simply upgrade to a proxy server that is compatible with your region or site.
What does private proxy mean and how can one get a private proxy?
Private proxies, as the name implies, are specific IPs developed to be utilized by an individual or firm. They are not to be utilized in pairs and appear to deliver better security and anonymity when compared to public or shared proxies as they have a limited number of users on them. You can get a private proxy by buying one from a proxy source or you can choose to create your server with its entry limited to approved users.
How does a proxy operate with Secure Socket Layers (SSL)?
Proxies, in general, can obstruct as well as filter secure socket layer encoded traffic, giving room for review of online data traffic. In further detail, SSL proxies function to obstruct encoded traffic and decode it right before it is transmitted to where it is sourced. Such ability gives the proxy the added advantage of offering top-notch security and enhanced performance. This also helps to push for a higher degree of anonymity.