Common Proxy Types and Everything You Should Know About Them
Proxies present enormous benefits, especially in the extraction of valuable data, direction of web traffic, and enhanced security and privacy. By acting as intermediaries between a client and a web server, firewalls and geo-restricted platforms can be bypassed for easier access to educational materials, online gaming, torrents, and valuable data.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll be exploring the concept of a proxy, how it works, and the common proxy types out there.
Keep reading!
What is a Proxy?
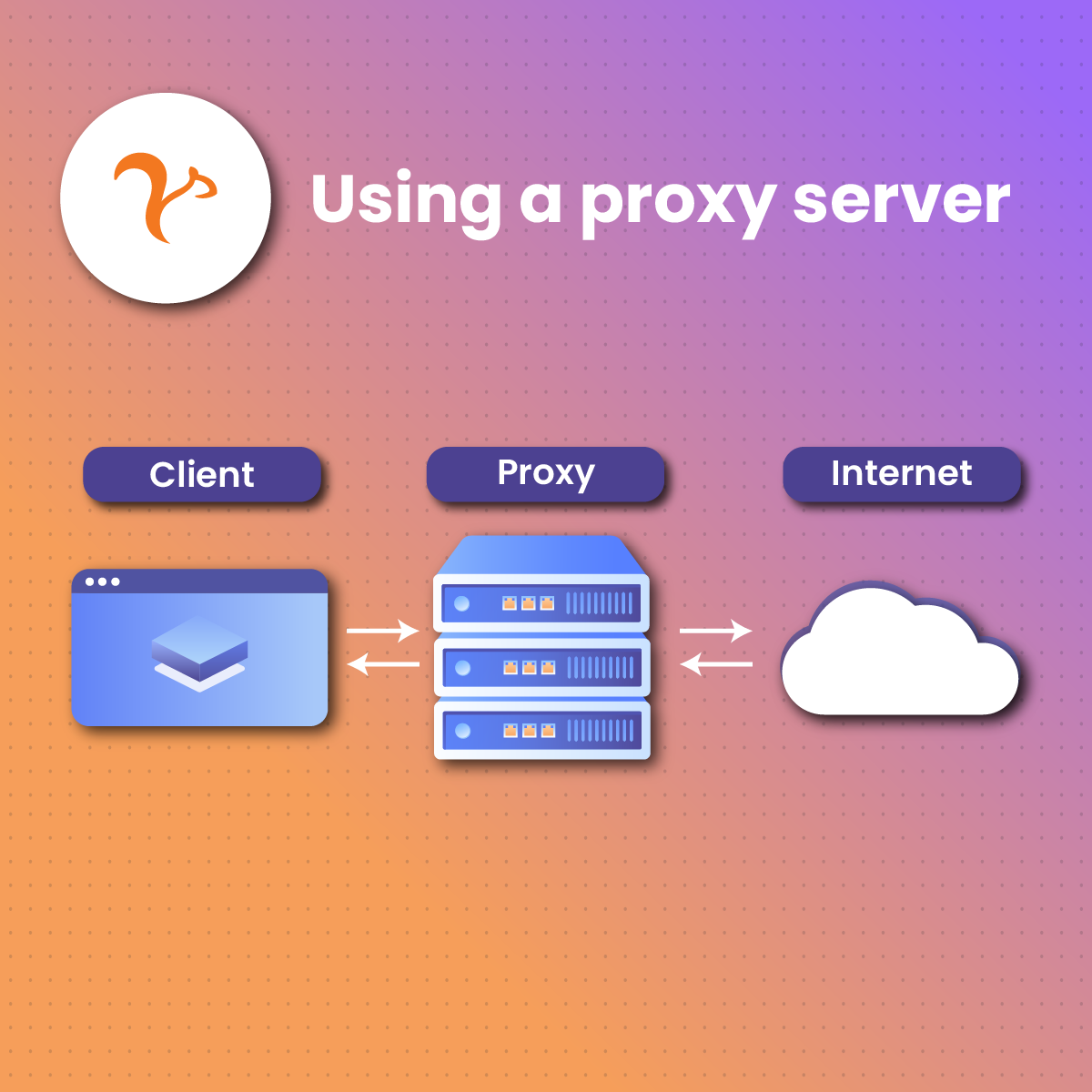
In simple terms, a proxy is a server that serves as a bridge between a user’s device and the internet. It can also be likened to a protection that shields a client from the internet. As the intermediary between an end-user (you and your device) and a more extensive server (internet), proxies help to prevent cyberattacks.
When you surf the internet looking for valuable pieces of information, the IP address of your device is usually exposed. It gets even worse when you randomly consent to cookies and other data-sharing policies without carefully reading the terms and conditions. Some of these websites may be fraudulent.
With your device’s information littered online, it makes it easy for cybercriminals lurking by the doors of the internet to track you, your IP address, and your device. But a proxy server prevents all of these by shielding your IP address and all data traffic between your device and the internet, enhancing privacy and anonymity.
As we go further, we’ll get to see how a proxy works and the proxy types we have out there.
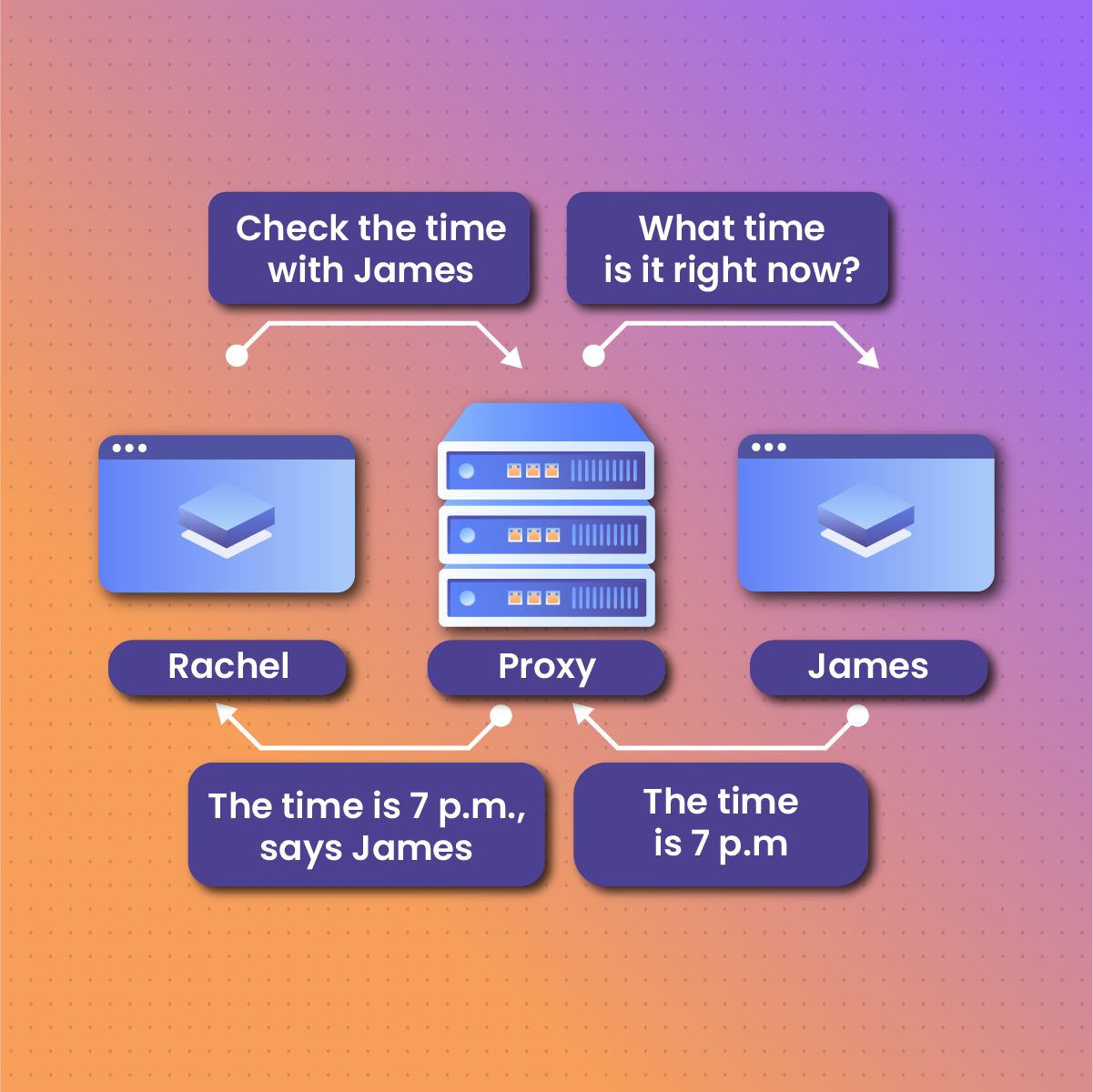
How a Proxy Works
It’s easy to conceptualize how a proxy works. It’s like a protective gate between your computer and the internet. When you open your browser (Google Chrome, Bing, or Explorer) on your device and make a search request, the proxy doesn’t allow your device to interact with the internet directly. Rather, it’ll mask your IP address and route your request to the internet with a different address.
When the internet processes the request and generates a response, it’s sent to the proxy server’s IP address, and finally to your computer. This helps you to remain anonymous while interacting with the internet.
Common Proxy Types
Proxies play a crucial role in ensuring privacy and security when a client surfs the internet. Different proxy types exist and they all fall under several categories – from server-based protocols to traffic flow, service, IP, location, and anonymity-based proxies.
We’ll be looking at each proxy category and the common examples that fall under it.
Server-Based Protocols
This is where all proxy protocols belong. From SOCKS proxies to FTP proxies. In this section, we’ll be exploring seven of these proxies.
-
SOCKS Proxy
A SOCKS proxy (Socket Secure) is a protocol that fosters communication between a client’s computer and a website or application where a firewall exists. SOCKS works in a way that it can route traffic for a client using another server called a TCP while also hiding the user’s IP address and server during online activities such as gaming, torrenting, and file-sharing.
By bypassing clusters hosted in a cloud behind a firewall, SOCKS proxies allow users to access applications or web pages that have some kind of restriction.
Two common kinds of SOCKS proxies are SOCKS4 and SOCKS5, with the latter being the newest edition. While SOCKS5 supports functionalities such as authentication, TCP, IPv6, and UDP, SOCKS4 provides proxy functionalities too but lacks support for authentication, UDP, and IPv6.
-
DNS Proxy
A domain name system (DNS) proxy is an intermediary that exists between a DNS client and server to foster communication. It often allows the client to use devices such as SRX-300, -320, -340, -345, -550M, and -1500. In the processing of DNS queries, the proxy issues new DNS resolution queries to each name server as it detects them.
It then caches older domain lookups to optimize the performance of present lookups. When a DNS request is made, it doesn’t go directly to the DNS server. Instead, it goes through the proxy and vice-versa.
-
HTTP Proxy
HTTP proxies are quite popular. They filter the traffic that should ordinarily flow between a client and the internet. While they are capable of hiding a user’s IP address during online activities, they scrutinize the results generated by online sources before they relay them to the end user. By acting as a content filter, viruses and other malware that can harm a user are thrown out.
-
SSL (HTTPS) Proxy
A secured socket layer (SSL) proxy is a server that enhances the transfer of data between a user’s device and the internet under encrypted conditions. The security in this setup relies mainly on the SSL proxy certificate and the public-private exchange key pairs.
This feature allows the proxy to validate a web server’s certificate and further checks which key to encrypt or decrypt. This proxy has two different keys, one for the server and the other for the client. It also relays all HTTPS traffic to the HTTP proxy for optimization.
-
FTP Proxy
The FTP proxy works with the file transfer protocol to control connections from the start point to the endpoint. By using different source and destination addresses and authentication, this proxy controls certain file prompts including the put and get.
Generally, FTP proxies protect your server from overflow attacks and malware by controlling the kind of file that downloads on your device. You don’t just control file download but also set the maximum username, password, filename, and command line length, ensuring your privacy and security.
-
CGI Proxy
Common Gateway Interface or CGI proxies act as an intermediary to route your IP address when interacting online, ensuring you remain anonymous. It can also be viewed as a sub-website that leads the way to the wider internet space.
CGIs are compatible with HTTPS, HTTP, FTP, and TCP protocols which make them popular. A common example of CGI is the Backconnect gateway protocol. The CGI could take a Weblet format where a series of codes on a web page form an interface, a form with entry submissions made in it, or a proxy built using CGI technology.
Access-Based Proxies
Another major category of proxies is based on how the proxy can be used. It could be private, or public. Let’s explore each of them below.
-
Public Proxy
These are also commonly referred to as open or shared proxy servers. The proxies are usually open for anyone who has a connection to the internet to access them. They are the cheapest proxies out there and they can come for free. While the infrastructure is just great for several people to be connected at the same time, they are easily spotted by websites that are notorious for blocking IP addresses.
Generally, they’re cheap and shareable, making privacy and anonymity inclusive for just anybody.
-
Private Proxy
Often interchanged with a dedicated proxy, private proxies give a client exclusive access to the IP addresses contained in its pool. These proxies could have some authentication mechanisms that allow only one verified user to access them.
Compared to the shared proxies, these provide a greater level of anonymity and privacy but are one of the priciest in the market. If you value privacy and are worried about the price of dedicated proxies, you can compare several options in the market to get the best deal.
IP-Based Proxies
This category classifies proxies based on the nature of IP addresses. Are the addresses from a Data Center, Residential, or Mobile source? Let’s explore this section below.
-
Data Center Proxies
Data Centers provide IP addresses to ensure the anonymity of clients while on the internet. These IP addresses are artificial and aren’t affiliated with internet service providers. The IP addresses are cheap but not real which makes output more quicker.
On the flip side, they aren’t reliable because Data Center IP addresses can be easily spotted by web servers and blocked.
-
Residential Proxies
These proxies have inter-woven and real IP addresses in their pools. They help users get access to websites or applications that are blocked due to location. Because these IP addresses are real and linked to internet service providers (ISPs) they are pricey and difficult to block compared to Data Center IP addresses.
Residential proxies could be static where a user is provided with just a single IP address during interface with the internet. Since it’s just one IP address that’s assigned to a user, the client’s device can be blocked from a web server.
In the case of rotational residential proxies, a user has access to a pool containing vast IP addresses and is usually assigned a new IP address after browsing the internet for a certain period. Because the IP address constantly changes, a user’s device cannot be blocked easily.
-
Mobile Proxy
These proxy servers use IP addresses from mobile data be it 3G, 4G, or 5G. When a client accesses the internet, it appears they’re using a mobile device. Even though they can easily access blocked web pages, mobile proxies can be locked out easily because mobile IP addresses are easily spotted.
Anonymity Level-Based Proxies
Looking at proxy types based on anonymity level just categorizes them based on the security they provide clients. Based on this, we have three different proxy types and each is explored below.
-
Transparent Proxy (Level 3)
This is basically an anonymity level-3 proxy that doesn’t shield your IP address. However, it lets you bypass or enforce certain restrictions by reducing a website’s cache so it loads quickly. It’s less private compared to other proxies in this category because your real IP address and the proxy you’re using can be seen when you request your browser.
-
High Anonymity (Elite) Proxies (Level 1)
These are usually advanced proxies that offer first-level security. They completely mask your IP address and web servers wouldn’t be able to spot if you’re using a proxy or not. They offer the best security and only expose the IP address of the proxy you’re using while surfing the internet.
-
Anonymous Proxies (Level 2)
While these proxies may provide clients with security, it’s usually in-between. With such proxies, it’s easier for web servers to spot if they are in use. Their security and anonymity level is at an average point, hence described as level 2.
Setting and Configuring Proxies
Setting up and configuring your proxy server is a technical task. Fortunately, we’ve explained how you can do this with just a few navigation and clicks.
To get the best result, it’s important to patronize a trusted proxy service provider and get a protocol that’s compatible with the device or interface you want to use – Windows, MacOS, Smartphone, Tablet, or Google Chrome. It’s necessary to retrieve all proxy details, including login and authentication credentials.
To set up and configure the proxy, use the following steps:
- Click the Start Icon, navigate to Admin Panel, Click on Network, and then Proxy (Start>Amin>Network>Proxy).
- Once you click on Proxy, you’ll be redirected to add the proxy information.
- Enter the IP address and the HTTP port number.
- Proceed to enter the authentication details which include a username and password.
- Click Save and your proxy will be fully activated, allowing you to enjoy privacy and security during online activities.
Bottom Line
Proxies are now extensively useful for not just bypassing firewalls or blockers that exist on the internet but also for enhancing privacy and anonymity. In this article, we explored the concept of proxies and how they work.
We further looked at the various proxy types in the market under four major categories based on server, IP address, access, and anonymity level.
We concluded by exploring how to set up and configure your proxy at a general level.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which proxy server should I choose for my business?
Choosing a proxy server is about preferences. When it comes to business, your decision should align with your goals. The proxy you choose should allow you to access any corporate data, help in your growth and marketing efforts, and give your business enhanced privacy and security.
How can I find the best proxy service providers?
Finding the right proxy service provider is pretty easy. Several service providers exist but the one you choose to patronize should have some or all of the features listed below”
- Super speed
- Hybrid network
- A wide variety of proxies
- Auto IP rotation
- 24/7 customer support
Which proxy based on anonymity level is the best?
All proxies serve different purposes, from bypassing geo-restricted sites or applications to enhanced privacy and security. Based on privacy level, proxy types could be transparent, anonymous, or high-anonymous.
With transparent proxies, a user’s IP address and proxy type are exposed on the internet. But it’s different with high-anonymous proxies as a client’s IP address and proxy details are concealed, providing more security. If your goal is enhanced safety, high-anonymity proxies will be just perfect.